Section: New Results
Assistance for Older Adults in Serious Game Using an Interactive System
Participants : Minh Khue Phan Tran, François Brémond, Philippe Robert.
Keywords: Older Adults, Assistance, Serious Games
Serious Games offer a new way to older adults to improve their abilities such as vision, balance or memory. However, cognitive impairment causes a lot of difficulties to them when actively practising these games. Their engagement and motivation are reduced rapidly when encountering successive problems without any help. Our hypothesis is that this problematic situation can be handled if they are assisted regularly. We propose then an interactive system which can determine dynamically the situations and provide different helps in real-time. We focuse on two main problems that the older players encounter regularly :
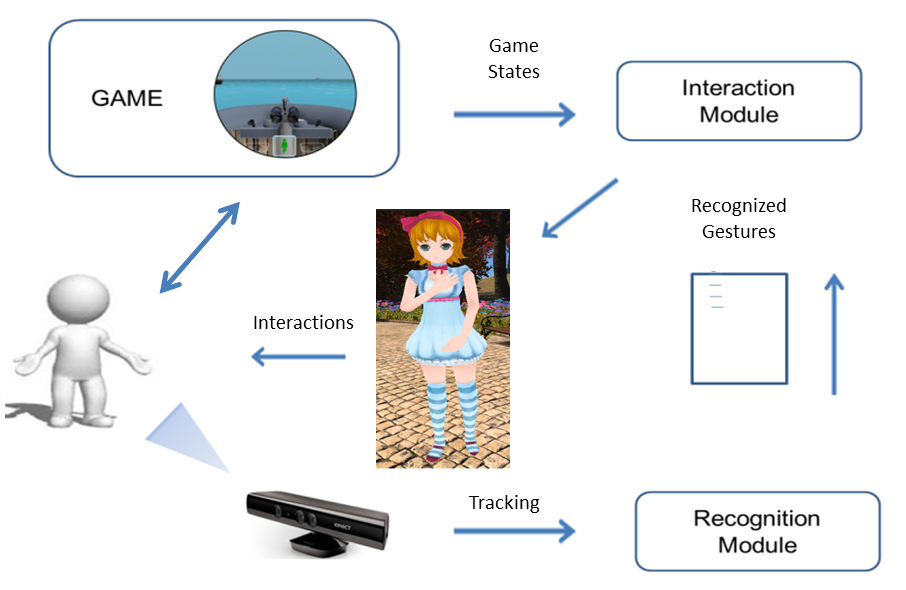
The system determines the above problems by computing various characteristics of the player (skeleton, postures, gestures ...) along the game states. This process is presented in Figure 24 . The characteristics of the player, which are collected by the Recognition Module thanks to Kinect Camera and the related SDK, are sent to the Interaction Module. This module associates these data with the game states provided by the game in order to recognize the problem and interacts with the player through a 3D-animated avatar.
The system is tested with 3 groups of patients described by 3 different cognitive states : mnesic plaints, MCI and Alzheimer. The patients are invited to play a concentration-based game with a Kinect camera. Each patient plays 3 phases : playing with therapist, playing alone and playing with the avatar. The playing time and the final score of each game phase are recorded. Here, the system takes into account the player's gestures and the game states for recognizing two situations :
The experimental results confirmed our hypothesis. Most of the patients have the best performance in phase "playing with the avatar". Their playing time is shorter and their final score is higher in phase "playing with assistance" than in phase "playing alone". The results are presented in the publication [36] accepted by the Games and Learning Alliance Conference in December 2015. Future work aims at improving the system and compare its efficiency with the one of "humans assistances".